Probability Statistics for Engineers Scientists
Teks penuh
Gambar
![Figure 6.1: The density function for a random variable on the interval [1, 3].](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok/2188134.1617974/3.520.187.427.69.207/figure-density-function-random-variable-interval.webp)
Garis besar
Dokumen terkait
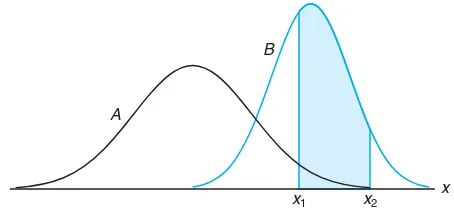
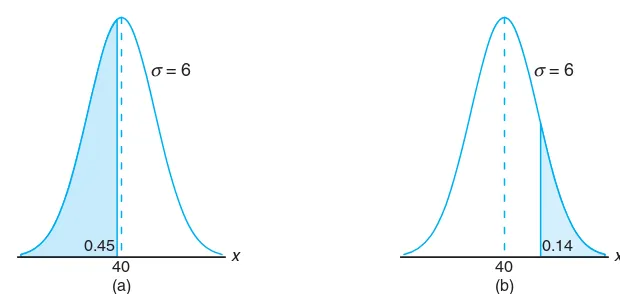
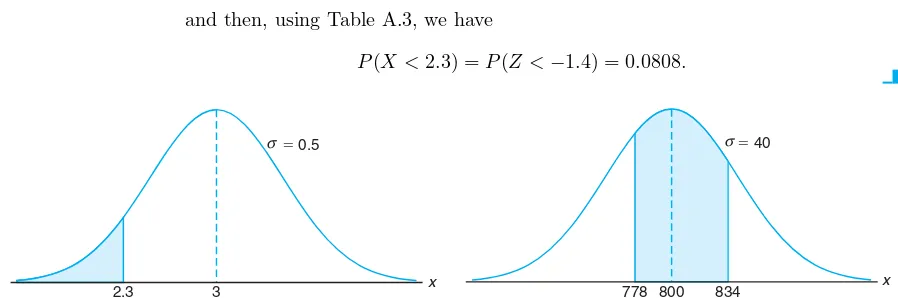
One can glean from the two examples above that the sample information is made available to the analyst and, with the aid of statistical methods and elements of probability,
Use the binomial expansion to find the probabilities of the various combinations of heads and tails... You draw from jars 2 and 4 200 times and get the
In the case of tossing a coin three times, the variable X, representing the number of heads, assumes the value 2 with probability 3/8, since 3 of the 8 equally likely sample
4.84 Referring to the random variables whose joint probability density function is given in Exercise 3.41 on page 105, find the expected weight for the sum of the creams and toffees
It is necessary for the data analyst to focus on an appropriate fit to the data and use inferential methods discussed in this chapter. Hypothesis testing on the slope of the
Example 12.11: Using the techniques of stepwise regression, find an appropriate linear regression model for predicting the length of infants for the data of Table 12.8.. Solution :
In such a case, if X is the random variable denoting the number of blue marbles chosen (successes) in n trials, then using the binomial distribution (1) we see that the probability
A Measurement Technique Based on Standard Normal Scores 143 Chapter Summary 147 Problems 148 Chapter 9 The Binomial Probability Distribution 151 Binomial Probabilities 151 The